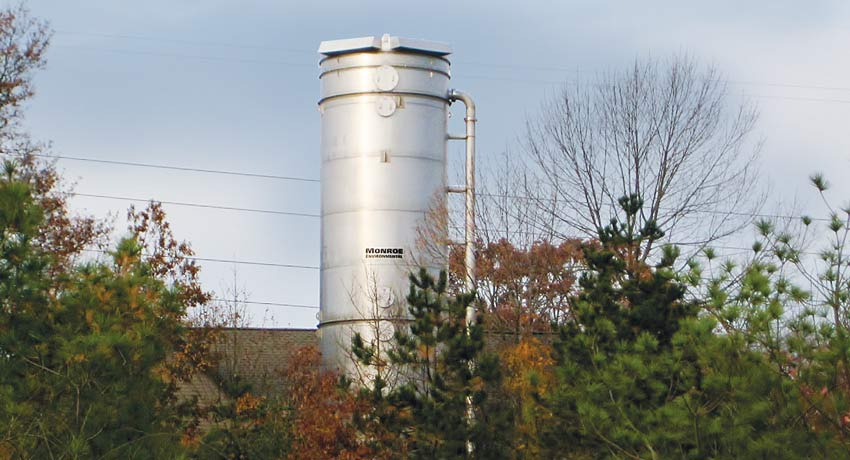
Ammonia Removal From Water By Air Stripping

Ammonia stripping works well with wastewater that has ammonia contents between 10 to 100mg l.
Ammonia removal from water by air stripping. Abstract ammonia removals of up to 90 from lime clarified filtered wastewater were obtained in a five stage counter current cross flow stripping tower using air to liquid rates of 400 to 500 ft gal. Loop can be used. This tower is an apparatus that removes only isolated nh3 by air stripping. To model the ammonia removal rate via air stripping technique using the water sparged aerocyclone.
This study reports an ammonia removal by an air stripping tower which is filled up with packing bed intalox saddles. As long as the air temperature and ph remain stable the operation of ammonia stripping is relatively simple and is unaffected by wastewater fluctuation and toxic loads. Furthermore k l a values of 0 017 0 027 1 s and htu ol values of 2 2 4 8 cm can be obtained in the pilot scale rpb at q l of 5 l min q g of 1500 l min and ω of 480 1000 rpm which account for the η greater than 95 at a t l of 4 6 min. Must dispose of concentrated ammonia sulfate.
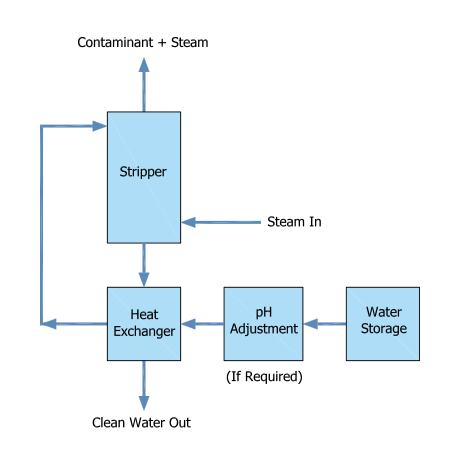
Additionally the input volume flow. To advance the design and problem solving the input and output ammonia are assumed to be 300 and 30 ppm respectively. The final technique air stripping is a physical process for ammonia recovery tolerating some degree of solids and requiring mainly temperature and ph controls. For higher ammonia content more than 100mg l it may be more economical to use alternate ammonia removal techniques such as steam stripping or biological methods.
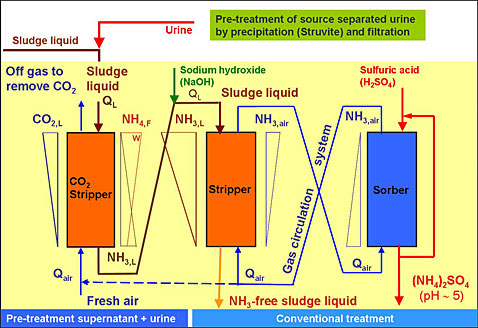
The variation of stripping efficiency was also studied as a function of the inlet ph of the water and the ratio of the air to liquid rate. Decreases in operating temperatures from 78 f to 43 f during the cold weather reduced the stripping efficiency by 30 and caused icing in the tower. In the closed loop the air is sent to an absorber where concentrated ammonium sulfate is formed. Air stripping is commonly used to remove the ammonia in multistage treatment systems for municipal landfill leachate lfl.
In vitro removal the study has revealed. Leachate quality and configuration of the treatment reactor were important factors affecting the efficiency of ammonia removal by stripping. This paper proposes a novel approach combining the process of stripping with biological removal of ammonia based on simultaneous nitrification and denitrification snd in a single hybrid sequencing batch reactor hsbr. The stage of nh3 and nh4 is affected by ph and temperature.
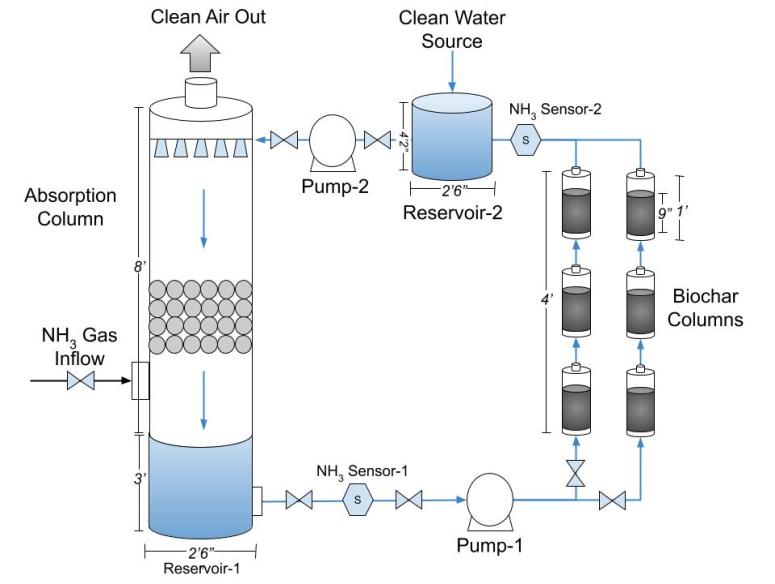
Ammonia is a very soluble gas in water. The clean air is then recycled back to the stripper. It was found that the water sparged aerocyclone removed ammoniacal nitrogen total phosphorus and cod from wastewater at 91 0 99 2 and 52 0 respectively. Water air and soil pollut 94 209 221.
Compared to traditional air strippers the continuous flow rpb appears to be a very efficient mechanism for ammonia stripping in terms of achieving. Adopted developed by matter muller et al.